Layout Composition
Abstract Layout
Most interface toolkits employ the concrete layout model, that is, control
positioning in the dialog is absolute in coordinates relative to the top-left
corner of the dialogís client area. This makes it easy to position the controls
on it by using an interactive tool usually provided with the system. It is also
easy to dimension them. Of course, this positioning intrinsically depends on the
graphics systemís resolution. Moreover, when the dialog size is altered, the
elements remain on the same place, thus generating an empty area below and to
the right of the elements. Besides, if the graphics systemís resolution changes,
the dialog inevitably will look larger or smaller according to the resolution
increase or decrease.
IUP implements an abstract layout concept, in which the positioning of
controls is done relatively instead of absolutely. For such, composition
elements are necessary for composing the interface elements. They are boxes and
fillings invisible to the user, but that play an important part. When the dialog
size changes, these containers expand or retract to adjust the positioning of
the controls to the new situation.
Watch the codes below. The first one refers to the creation of a dialog for
the Microsoft Windows environment using its own resource API. The second uses
IUP. Note that, apart from providing the specification greater flexibility, the
IUP specification is simpler, though a little larger. In fact, creating a dialog
on IUP with several elements will force you to plan your dialog more carefully Ė
on the other hand, this will actually make its implementation easier.
Moreover, this IUP dialog has an indirect advantage: if the user changes its
size, the elements (due to being positioned on an abstract layout) are
automatically re-positioned horizontally.
The composition elements includes vertical boxes (vbox), horizontal
boxes (hbox) and filling (fill). There is also a depth box (zbox)
in which layers of elements can be created for the same dialog, and the elements
in each layer are only visible when that given layer is active.
|
in Windows |
in IupLua |
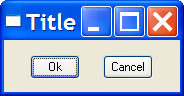
dialog DIALOG 0, 0, 117, 32
STYLE WS_MINIMIZEBOX | WS_MAXIMIZEBOX |
WS_CAPTION | WS_SYSMENU |
WS_THICKFRAME
CAPTION "Title"
BEGIN
PUSHBUTTON "Ok",IDOK,17,9,33,15
PUSHBUTTON "Cancel",IDCANCEL,66,9,33,15
END
|
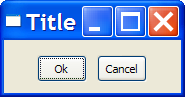
dialog = iup.dialog
{
iup.hbox
{
iup.fill{},
iup.button{title="Ok",size="40"},
iup.button{title="Cancel",size="40"},
iup.fill{}
;margin="15x15", gap="10"
}
;title="Title"
}
|
|
 |
 |
Now see the same dialog in LED and in C:
|
in LED |
in C |
dialog = DIALOG[TITLE="Title"]
(
HBOX[MARGIN="15x15", GAP="10"]
(
FILL(),
BUTTON[SIZE="40"]("Ok",do_nothing),
BUTTON[SIZE="40"]("Cancel",do_nothing),
FILL()
)
)
|
dialog = IupSetAttributes(IupDialog
(
IupSetAttributes(IupHbox
(
IupFill(),
IupSetAttributes(IupButton("Ok", NULL), "SIZE=40"),
IupSetAttributes(IupButton("Cancel", NULL), "SIZE=40"),
IupFill(),
NULL
), "MARGIN=15x15, GAP=10")),
), "TITLE=Title")
|
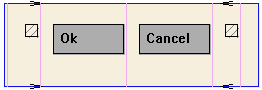
Following, the abstract layout representation of this dialog:
|
Layout Hierarchy |
Layout Visualization |
Dialog
HBox
Fill
Button
Button
Fill
|
 |


